Binary Search Tree Iterator
Problem
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example
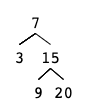
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
My Answer
- 작은 순서로 탐색하는것은 BST의
In-order탐색이다, Binary Tree Inorder Traversal BSTIterator의 생성자에서,Queue(m_q)를 구성한다.next()에선m_q.poll()하면된다.hasNext()에선m_q가 비어 있지만 않으면true이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
Queue<Integer> m_q;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
m_q = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while(curr != null || !s.isEmpty()) {
while(curr != null ) {
s.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
curr = s.pop();
m_q.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
return m_q.poll();
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return !m_q.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/
Fastest Answer
nxt가 다음 노드를 가리키는 객체이다.next()에선 다음 노드의 값을 반환함과 동시에nxt의 값을 다음next()가 호출될때 사용할 값으로 할당한다.right값이null인것을 이용해서 다음 노드와의 연결을 만든다.left가null인 경우엔next()의 타겟이 되는 노드는nxt이고, 다음 노드는nxt.right가 된다.- 예를 들어 예제는 다음과 같은 흐름으로 진행된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Input : [7,3,15,null,null,9,20] nxt = 7 next() nxt = 3, 3's right is 7 res = 3, nxt = 7 next() nxt = 7, 3's right is null res = 7, nxt = 15 ... 3의left,right둘 다 처음엔null이 였는데,next()호출에서right에7을 할당해서 다음 호출시 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
TreeNode nxt;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
nxt = root;
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
TreeNode res = null;
while (nxt != null) {
if (nxt.left != null) {
TreeNode pre = nxt.left;
while (pre.right != null && pre.right != nxt) {
pre = pre.right;
}
if (pre.right == null) {
pre.right = nxt;
nxt = nxt.left;
} else {
pre.right = null;
res = nxt;
nxt = nxt.right;
break;
}
} else {
res = nxt;
nxt = nxt.right;
break;
}
}
return res.val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return nxt != null;
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/