Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Problem
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
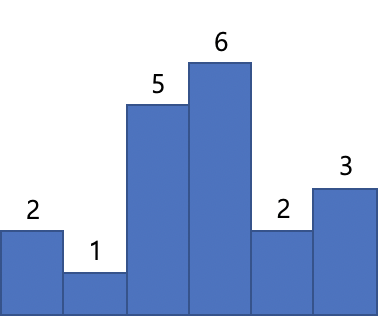
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
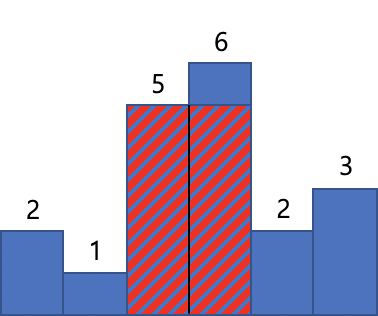
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
Example
1
2
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
My Answer
- 재귀를 이용해서 해결
backTracking함수의 파라미터로 기준이 되는index를 넘긴다.backTracking함수에서는startindex에 해당 하는pivot을 기준으로 좌,우의 값을 비교 해서 같거나 클때count를 증가 시킨다.while(prev >= 0 || next < length ) {구문 이후 최종 계산된count와pivot의 곱을 통해 현재 기준값으로 나올수 있는 최대 값을 구하고,- 재귀를 통해 그 다음
index에 해당 하는 값을 구해서Max비교 한다. - 모든 원소에 대해서 수행하기 때문에, 연산량이 많다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
return backTracking(heights, 0);
}
int backTracking(int[] heights, int start ){
if ( heights.length <= start) {
return 0;
}
int pivot = heights[start];
int count = 1;
int prev = start -1;
int next = start + 1;
int length = heights.length;
while(prev >= 0 || next < length ) {
if ( prev >= 0 ) {
if ( heights[prev] >= pivot ) {
count++;
prev--;
} else {
prev = -1;
}
}
if ( next < length ) {
if( heights[next] >= pivot ) {
count++;
next++;
} else {
next = length;
}
}
}
int total = pivot * count;
int next_total = backTracking(heights, start +1);
return Math.max(total, next_total);
}
}
Fastest Answer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
if (heights == null || heights.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return lra(heights, 0, heights.length);
}
private int lra(int[] heights, int start, int end) {
if (end - start == 1) {
return heights[start];
}
//start index에 해당 하는 값을 기준으로 최소 값을 구한다.
//start ~ end 사이 값들을 비교하면서, 요소들이 오름차순으로만 구성되어 있는지, 내림차순으로만 구성 되어 있는지, 아니면 뒤죽박죽 섞여 있는지 체크한다.
boolean ascd = true;
boolean desc = true;
int min = heights[start];
for (int i = start + 1; i < end; i++) {
if (heights[i] < min) {
min = heights[i];
}
if (heights[i] < heights[i-1]) {
ascd = false;
} else if (heights[i] > heights[i-1]) {
desc = false;
}
}
int max = min * (end - start); //위 반복문에 의해서 결정된 min값과 end-start의 곱이 곧 start 기준에 나올수 있는 최대 값이다.
if (ascd) { //오름 차순으로되어 있다면, start + 1 ~ end 까지 최대 값을 구해서 비교
for (int i = start + 1; i < end; i++) {
if (heights[i] == heights[i-1]) continue;
int tmp = heights[i] * (end - i);
if (tmp > max) {
max = tmp;
}
}
} else if (desc) { //내림 차순으로되어 있다면, 뒤쪽부터 작은 수 이기 때문에, end-2 ~ start 까지 최대 값을 구해서 비교
for (int i = end - 2; i >= start; i--) {
if (heights[i] == heights[i+1]) continue;
int tmp = heights[i] * (i - start + 1);
if (tmp > max) {
max = tmp;
}
}
} else {
boolean getStart = false;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (!getStart) {
if (heights[i] == min) continue;
start = i;
getStart = true;
} else {
if (heights[i] != min) continue;
int tmp = lra(heights, start, i);
if (tmp > max) {
max = tmp;
}
getStart = false;
}
}
if (getStart) {
int tmp = lra(heights, start, end);
if (tmp > max) {
max = tmp;
}
}
}
return max;
}
}