Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
Problem
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example
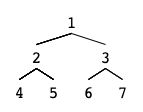 Figure A
Figure A
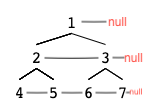 Figure B◊
Figure B◊
1
2
3
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
My Answer
- 반복문을 이용해서 해결
Depth별로 첫번째 노드 의 다음 노드는 두번째 이고, 두번째의 다음 노드는 세번째… 마지막 노드의 다음 노드는 null이다.Queue의 사이즈만큼 반복문을 수행하고, 반복을 수행 할 때 마다,curr을 변경하고,curr.next를 현재 노드로 할당하자.- 마지막번째 노드에서는 할당 하지 말고
curr에null을 할당 하면 된다. - 위 예제는 다음과 같은 흐름이 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
q = [1], for { i : 0 node = 1 curr = null q.add(2), q.add(3) } q = [2,3], for { i : 0 node = 2 curr = null q.add(4), q.add(5) i : 1 node = 3 curr = 2 curr.next = 3 = 2 -> 3 q.add(5), q.add(7) } q = [4,5,6,7], for { i : 0 node = 4 curr = null i : 1 node = 5 curr = 4 curr.next = 5 = 4 -> 5 i : 2 node = 6 curr = 5 curr.next = 6 = 5 -> 6 i : 3 node = 7 curr = 6 curr.next = 7 = 6 -> 7 }
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if ( root == null )
return null;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
Node curr = null;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int n = q.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
Node node = q.poll();
if ( curr != null ) {
curr.next = node;
}
if ( i < n - 1 ) {
curr = node;
} else {
curr = null;
}
if ( node.left != null )
q.add(node.left);
if ( node.right != null )
q.add(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}