The Skyline Problem
Problem
A city’s skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you are given the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program to output the skyline formed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).
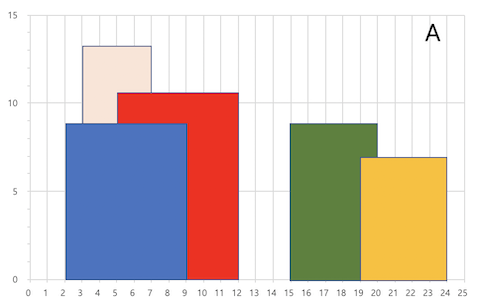
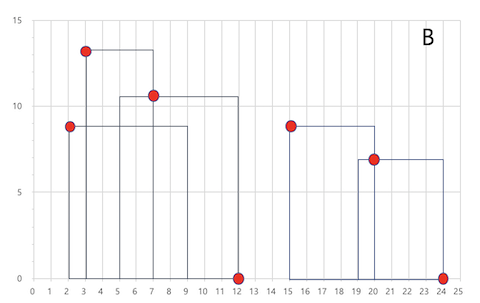
Buildings Skyline Contour
The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers [Li, Ri, Hi], where Li and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, and Hi is its height. It is guaranteed that 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] .
The output is a list of “key points” (red dots in Figure B) in the format of [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] that uniquely defines a skyline. A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Note
- The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range
[0, 10000] - The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position
Li - The output list must be sorted by the x position
- There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance,
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
My Answer
- 알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
- x좌표대로 진행 하면서, 높이 차가 발생할때 마다 결과 리스트에 넣으면 된다.
- 예제 처럼
[2 9 10]일때 2개의 좌표가 나온다.[[2 10], [9 10]]앞의 좌표는 빌딩의 시작 좌표이고, 뒤의 좌표는 빌딩의 끝 좌표 이다. -
[3 7 15]까지 추가 되면[[2 10], [9 10], [3 15], [7 15]]가 된다. 이걸 그림으로 표현 하면 다음과 같다.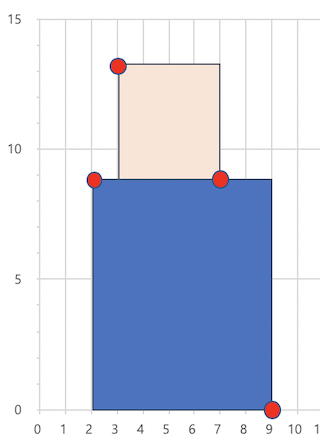
빨간 점은 결과 리스트에 들어가야한 좌표들
[[2 10], [3 15], [7 10], [9 0]] - 위 그림에서 보듯이 결과 리스트에 들어가야하는 것들은 높이 차가 발생할때 라는것을 알 수 있다.
- 높이 차가 발생했다 라는것을 알기 위해서, 기존의 최대 높이
prev_max_h와 현재 좌표 입장에서의 최대 높이curr_max_h, 그리고 지금까지 거쳐왔던 높이들을 저장할 데이터 스트럭쳐queue_h가 필요 하다. - 처음
prev_max_h를 0으로 해서 좌표를 순회 하면서, 좌표가 빌딩의 시작 좌표인 경우엔queue_h에 현재 높이 를 넣고,curr_max_h에는queue_h에 있는 높이들중 가장 큰 값을 할당한다. - 만약
prev_max_h와curr_max_h가 다르다면, 높이차가 발생한 것이니 결과 리스트에 추가 하면 되는데,[현재 x, curr_max_h]형태로 추가하고, 6~7번을 반복한다. [[2 10], [9 10], [3 15], [7 15]]의 경우 다음과 같은 흐름이 된다.- 현재 좌표 =
[2 10],prev_max_h= 0,queue_h= [0, 10],curr_max_h= 10 prev_max_h와curr_max_h가 다르기 때문에, 결과 리스트에[현재 x, curr_max_h] = [2 10]추가prev_max_h에curr_max_h할당.prev_max_h= 10- 다음 좌표로 반복 수행
- 현재 좌표 =
- 6번 내용을 수행하기 이전에 정렬을 해줘야 한다. x좌표에 따라 순차 대로 진행 해야 하기 때문에,
[[2 10],[3 15],[7 15],[9 10]]로 6번을 시작 해야 한다.
- 각 x좌표에 따른 높이 값을 저장하는 구조체
Point를 만들자. - x좌표 별로
building의Li에 해당 하면isStart를true로 하고,Ri에 해당 하면isStart를false로 하자. - 총 생성되는
Point의 갯수는building의 갯수 x 2가 되고,points배열에 저장하자. points를 정렬 한다, 이때 정렬 조건은 다음과 같다.- x 좌표가 다르다면 x값이 작은것 우선
isStart가true라면높이가 큰 것 우선,isStart가false라면높이가 작은 것 우선
points를 순회 하면서, 높이들을 저장하면서, 높이가 큰 순서 대로 정렬될PriorityQueue를 준비 한다.- 현재
Point가isStart라면PriorityQueue에 넣고, 아니라면 뺀다. PriorityQueue의 제일 앞에 있는 값, 즉 높이가 가장 높은것을 가져온 후, 이전 순회에서 결정된 높이값과 비교해서, 다르다면 결과 리스트에 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
class Solution {
private class Point implements Comparable<Point>{
int x;
int height;
boolean isStart;
public Point(int x, int height, boolean isStart) {
this.x = x;
this.height = height;
this.isStart = isStart;
}
public int compareTo(Point p) {
if (this.x != p.x) { //x가 다른건 볼것도 없다, x값이 작은것을 우선하자.
return this.x - p.x;
} else { //x가 동일 하다면, this와 p가 isStart라면 높이가 큰것을 우선으로 하고, 아니라면 높이가 작은것을 우선 하자.
return (this.isStart ? -this.height : this.height) - (p.isStart ? -p.height : p.height);
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int total_count = buildings.length;
if ( total_count == 0 ) {
return result;
}
Point[] points = new Point[total_count * 2];
int i = 0;
for( int[] building : buildings ) { //building 하나 [Li, Ri, Hi]를 이용해서 2개의 Point를 만들자, [Li, Hi, true], [Ri, Hi, false]
points[i++] = new Point(building[0], building[2], true);
points[i++] = new Point(building[1], building[2], false);
}
Arrays.sort(points); //정렬을 반드시 해줘야 한다.
PriorityQueue<Integer> height_queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(Collections.reverseOrder()); //순회돌면서, 거쳐간 Point의 높이 값을 저장하고, 값이 큰 순서대로 저장할 Queue
height_queue.add(0); //기본 높이 0을 넣어 주자.
int prev_max_height = 0;
for( Point point : points ) {
if ( point.isStart ) { //시작 좌표라면 현재 Point의 높이의 시작이니까 넣어 주고, 끝 좌표라면 현재 높이는 처리 했다는 의미니까 빼주자.
height_queue.add(point.height);
} else {
height_queue.remove(point.height);
}
int current_max_height = height_queue.peek();
if ( prev_max_height != current_max_height ) { //이전 최고 높이와 현재 최고 높이가 다르다는것은 높이차가 발생했다. 결과 리스트에 추가 하자.
result.add(Arrays.asList(point.x, current_max_height));
prev_max_height = current_max_height;
}
}
return result;
}
}
Fastest Answer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<List<Integer>> keyPoints = new ArrayList<>();
int lastLowXIdx = -1;
for (int[] building : buildings){
int li = building[0];
int ri = building[1];
int hi = building[2];
lastLowXIdx = insertBuilding(li, ri, hi, keyPoints, lastLowXIdx);
}
return keyPoints;
}
protected int insertBuilding(int li, int ri, int hi, List<List<Integer>> keyPoints, int lastLowXIdx){
int nextIdx = keyPoints.size();
for (int i = lastLowXIdx + 1; i < keyPoints.size(); i++){ //기존의 결과리스트에 있는것들 중에서 현재 빌딩의 Li 보다 큰 x인것을 찾는다. 왜냐하면, 결과 리스트를 x값으로 정렬되어야 하기 때문.
if (keyPoints.get(i).get(0) > li){
nextIdx = i;
break;
}
}
int currIdx = nextIdx - 1; //좌표가 들어갈 결과 리스트의 index
int oldHight = currIdx >= 0 ? keyPoints.get(currIdx).get(1) : 0; //기존 결과 리스트에 있던 높이
int currentHigh = oldHight;
if (hi > oldHight){ //현재 빌딩의 높이가 기존 결과 리스트에 있던 높이 보다 크고
if (currIdx < 0 || keyPoints.get(currIdx).get(0) < li) { //현재 index가 0보다 작거나 ( 결과 리스트가 비어 있었다 ), x가 li보다 작다면 결과 리스트에 추가.
keyPoints.add(currIdx + 1, makeKeyPoint(li, hi));
currentHigh = hi;
currIdx++;
} else { //x가 li와 같다. 즉 같은 빌딩의 시작 위치가 동일한데, 높이가 다르다.
if (currIdx >= 1 && keyPoints.get(currIdx - 1).get(1) == hi){ //넣어야 할 위치 이전 결과 리스트의 값의 높이가 현재 높이와 동일하다. ???????
keyPoints.remove(currIdx);
currIdx--;
currentHigh = hi;
} else { //높이만 다시 갱신해 주자.
keyPoints.get(currIdx).set(1, hi);
currentHigh = hi;
}
}
} else {
currentHigh = oldHight;
}
lastLowXIdx = currIdx;
currIdx ++;
while (currIdx < keyPoints.size() && keyPoints.get(currIdx).get(0) < ri){ //기존의 결과 리스트의 x값들 중, Ri보다 작은것들, 즉 현재 빌딩이 추가 됨으로 인해서 없어져야 하거나, 높이 갱신이 필요한것들 처리
oldHight = keyPoints.get(currIdx).get(1);
if (hi >= oldHight){
if (currentHigh == hi){
keyPoints.remove(currIdx);
currIdx--;
} else {
keyPoints.get(currIdx).set(1, hi);
currentHigh = hi;
}
} else {
currentHigh = oldHight;
}
currIdx ++;
}
if (hi > oldHight && currentHigh != oldHight){
if (currIdx >= keyPoints.size() || keyPoints.get(currIdx).get(0) > ri) {
keyPoints.add(currIdx, makeKeyPoint(ri, oldHight));
currentHigh = oldHight;
}
}
return lastLowXIdx;
}
protected List<Integer> makeKeyPoint(int x, int y){
List<Integer> keyPoint = new ArrayList<>(2);
keyPoint.add(x);
keyPoint.add(y);
return keyPoint;
}
}